EU Battery Regulation explained
11 aug. 2023
What you need to know about the EU Battery Regulation.
Updated: 1 Nov 2024
In July 2023, a new EU battery regulation (Regulation 2023/1542) was approved by the EU. The aim of the regulation is to create a harmonized legislation for the sustainability and safety of batteries.
The regulation started to apply on 18 February 2024. Until 18 August 2025, the regulation will coexist with the Battery Directive (2006/66/EC). But from 18 August 2025, the regulation will be the main EU legislation for batteries since the Battery Directive is repelled to a great extent at that date. The new regulation includes many new legislative measures and, with time, additional obligations and requirements will be introduced.
The regulation consists of five parts that affect different stakeholders in the battery value chain. All parts are not applicable for all batteries. Instead, the regulation defines five battery categories depending on how the battery is used. Some requirements are only applicable for some battery categories.
- Portable batteries
- Light means of transport (LMT) batteries
- Starting, lighting and ignition (SLI) batteries
- Industrial batteries
- Electric vehicle (EV) batteries
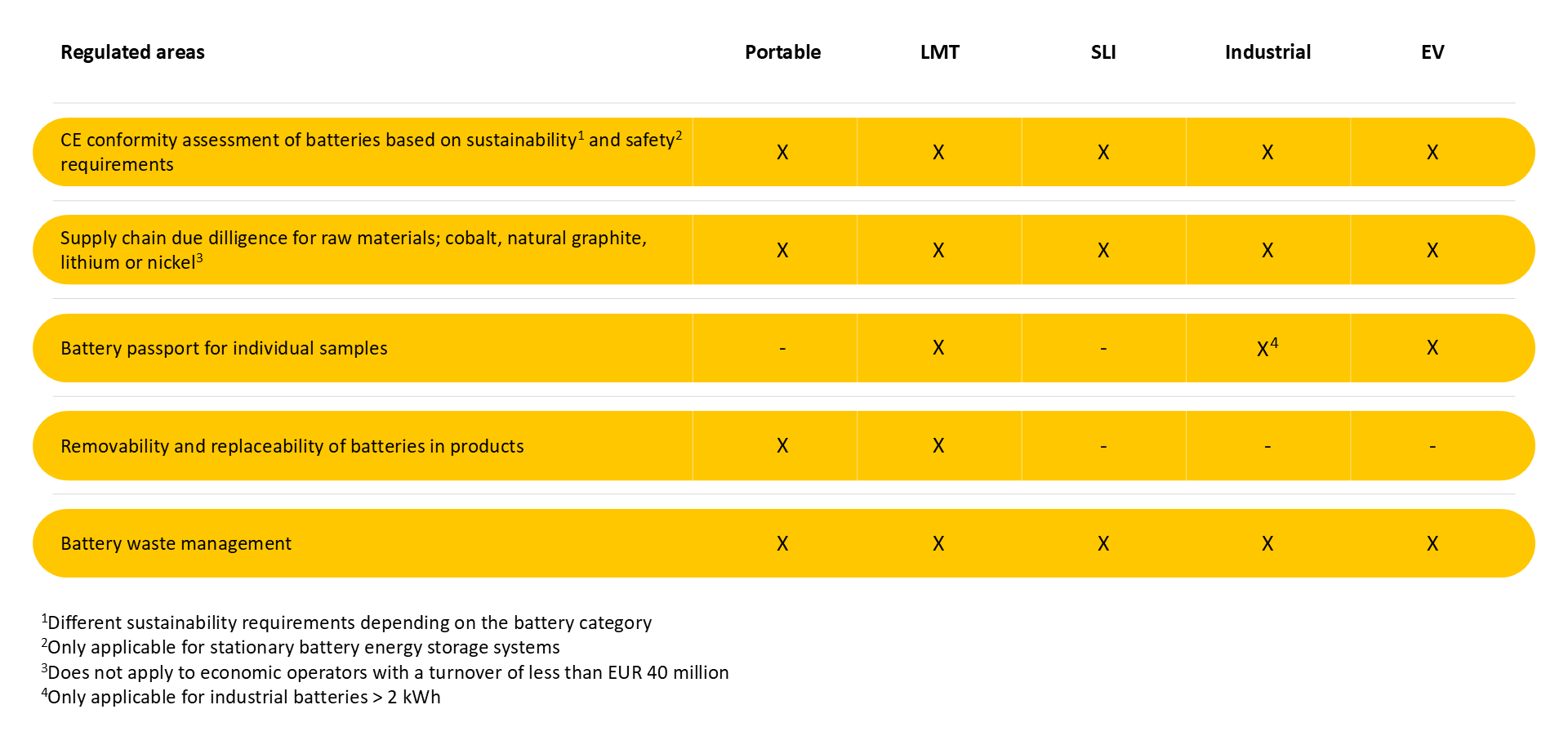
CE conformity assessment of batteries
Requirements associated with a new CE conformity assessment of batteries are introduced in the Regulation. This means that all batteries, regardless of whether they are used in a product or supplied separately, needs to be CE marked according to this regulation.
The CE conformity assessment and CE marking requirements started to apply on 18 August 2024. Initially, requirements for carbon footprint, recycled content and performance and durability requirements for portable batteries of general use will not be part of the CE-marking but will be added at a later date.
Generally, it is the battery manufacturer's obligation to take care of the CE conformity assessment, and the battery manufacturer needs to fulfill different requirements depending on in which product the battery will be used.
The CE conformity assessment is a self-certification process for portable batteries and industrial batteries with a capacity of less than 2 kWh. For all other batteries, a notified body will need to be involved when the requirements for a carbon footprint declaration and recycled content declaration start to apply.
The requirements that need to be considered for each battery category are:

The carbon footprint requirement will likely start to apply in late 2025/early 2026 for EV batteries and will be applicable to rechargeable industrial batteries (with internal storage) above 2 kWh the year after. It will also apply to LMT and industrial batteries (with external storage above 2 kWh), but no earlier than 2028 and 2030 respectively.
Recycled content and performance and durability requirements for portable batteries of general use will start to apply from 2028 and onwards, depending on the battery category.
Battery passport
The regulation introduces requirements for an individual electronic battery passport for each industrial battery (with a capacity of more than 2 kWh), EV battery and LMT battery (e.g., an e-bike battery). The electronic record should, among other data, include general information about the battery (e.g., indication of the battery manufacturer and geographical location of the battery manufacturing facility) and the data sheet of the battery. The aim with the battery passport is to enhance transparency along the supply and value chains for all stakeholders and to aid the exchange of information regarding each battery sample. The electronic passport should be accessible through a QR-code on the battery.
The battery passport obligation will start to apply on 18 February 2027, and it is the responsibility of the battery manufacturer/ importer to arrange the battery passport.
Supply chain due diligence obligations
Supply chain due diligence obligations are introduced for companies that place batteries on the EU market (i.e. battery manufacturers or importers) or put batteries into service (i.e. battery manufacturers that use the batteries themself). The obligations are applicable for the raw materials cobalt, natural graphite, lithium, or nickel. Companies with a net turnover of less than 40 million EUR, that are also not part of a group which on a consolidated basis exceeds the limit of 40 million EUR, are exempt from the obligation.
It is required that the company should:
- Adopt and communicate a company due diligence policy for batteries.
- Establish strong company management systems (to support the due diligence policy).
- Identify and assess risks in the upstream supply chain.
- Design and implement a strategy to respond to identified risks.
The regulation requires a third-party verification (performed by a notified body) of the due diligence policies and how the policies are implemented in the management system. The supply chain due diligence obligation will start to apply on 18 August 2025.
Battery waste management
Extended producer responsibility for batteries and registration obligations already exists in the EU battery directive. Extended producer responsibility means that companies that first make batteries available on the market in a member state are responsible for the end-of-life collection and treatment of the batteries in that member state. In the new regulation, the EU introduces new updated targets for collection rates and recycling efficiencies. The extended producer responsibility and registration requirements in the new regulation will apply from 18 August 2025.
The regulation introduces targets for material recovery of cobalt, copper, lead, lithium and nickel in recycling and treatment facilities of batteries. The targets will start to apply from 31 December 2027.
Replaceability of batteries
The regulation introduces requirements that say that portable batteries should be easily removable and replaceable by the end-user at any time during the lifetime of the product, and that LMT batteries and cells in LMT batteries should be easily removable and replaceable by an independent professional at any time during the lifetime of the product. The requirements will start to apply from 18 February 2027.
How Intertek can help
The EU Battery Regulation will have a large impact on manufacturers of battery-operated products, appliances, and vehicles, as well as on the whole battery industry.
Intertek has more than 50 years of experience evaluating all kinds of batteries, serving developers, manufacturers, and application experts worldwide. We have world-class accredited testing laboratories and are globally recognized for our independence and sound advice. Intertek evaluates more than 20,000 batteries annually and our team of experienced battery experts stand ready to support our clients to prepare to adhere to these new requirements.
If you want to learn more about this regulation, Intertek Academy holds three-hour online courses about the regulation. You can register here:
https://www.intertek.se/academy/courses/eu-battery-regulation/
Intertek can also support with a regulative gap analysis focused specifically on a product or a set of products that contain batteries. The gap analysis would identify new requirements, obligations, who is responsible for fulfilling these requirements and obligations and when they start to apply.
